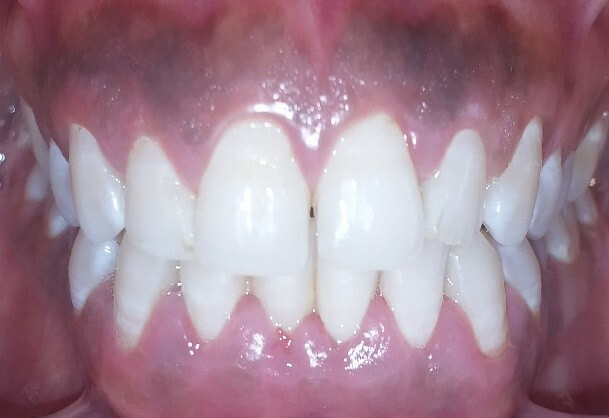
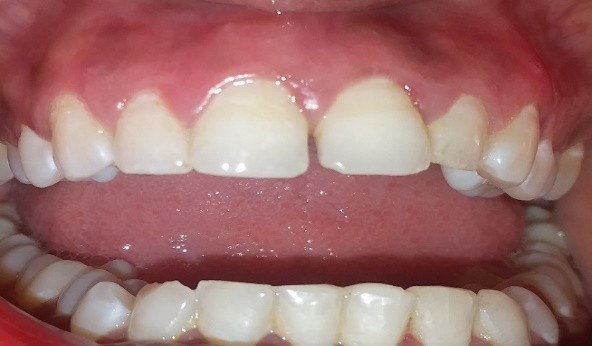
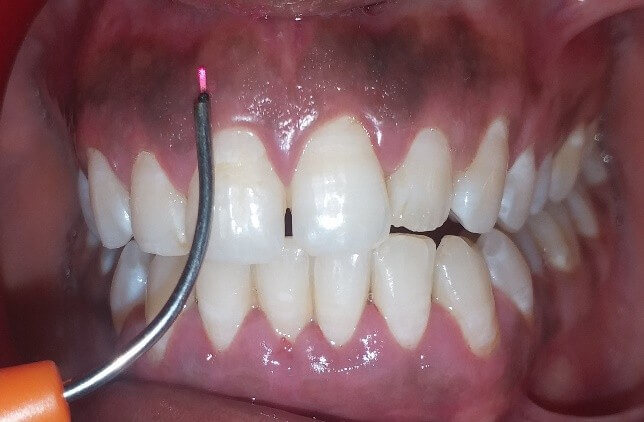
Gum health and appearance are important components for an attractive smile, and the removal of unsightly pigmented gum is needed for a confident smile. Melanin, carotene, reduced hemoglobin, and oxy-hemoglobin are pigments that lead to gum color and induce hyperpigmentation, which can be treated with gum depigmentation.
The excessive accumulation of melanin in the superficial layer of gums induces gums hyperpigmentation. Melanin is a pigment found in the skin that gives it its colour. Gum pigmentation may appear as a diffuse dark purplish discoloration or as irregularly coloured brown, light brown, or black spots.
Melanin pigmentation has been linked to drugs like minocycline, zidovudine, chlorpromazine, ketoconazole, bleomycin, and cyclophosphamide.


Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.